This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison
LDLR Gene Ontology
Initial ontology searches were done using AmiGO, and the associated terms are listed below.
Biological Process
These GO terms involve processes that occur within a cell or a part of a pathway. As stated here, it can be difficult to separate biological process from molecular function. Most of these terms associate with LDLR and its involvement with cholesterol maintenance. However, LDLR also responds to estrogen, which is somewhat unexpected. This function of the protein is of interest and will be further looked in to.
Cholesterol homeostasis
Cholesterol metabolic process
Cholesterol transport
Endocytosis
Interspecies interaction between organisms
Intestinal cholesterol absorption
Lipid metabolic process
Lipid transport
Lipoprotein catabolic process
Low-density lipoprotein particle clearance
Protein amino acid O-linked glycosylation
Response to estrogen stimulus
Steroid metabolic process
Cholesterol metabolic process
Cholesterol transport
Endocytosis
Interspecies interaction between organisms
Intestinal cholesterol absorption
Lipid metabolic process
Lipid transport
Lipoprotein catabolic process
Low-density lipoprotein particle clearance
Protein amino acid O-linked glycosylation
Response to estrogen stimulus
Steroid metabolic process
Cellular Component
These GO terms specify the location, organelle, or sub-organelle where the gene product localizes. All terms associated with LDLR were expected except for Low-density lipoprotein particle. LDLR binds LDL, but this term does not seem to fit within the cellular component ontology. The definition of cellular component can be found here.
Caveola
Clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane
Coated pit
Endosome
Endosome membrane
Integral to plasma membrane
Low-density lipoprotein particle
Plasma membrane
Clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane
Coated pit
Endosome
Endosome membrane
Integral to plasma membrane
Low-density lipoprotein particle
Plasma membrane
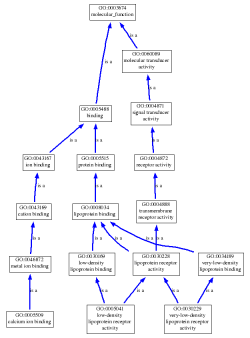
Molecular Function
These GO terms relate to the specific action of proteins or complexes at the molecular level. The definition of molecular function can be found here. The only unexpected finding is the very-low density lipoprotein receptor activity term. Perhaps this term is listed because LDLR and VLDLR are paralogous genes and have similar functions. Gene paralogs result from ancestral gene duplication and over time the genes are able to evolve to have distinct function. A website explaining paralogs can be found here.
Calcium ion binding
Lipoprotein binding
Low-density lipoprotein receptor activity
Protein binding
Transmembrane receptor activity
Very-low density lipoprotein receptor activity
Lipoprotein binding
Low-density lipoprotein receptor activity
Protein binding
Transmembrane receptor activity
Very-low density lipoprotein receptor activity
Analysis
Almost all of the GO terms found using AmiGO were expected, based on LDLR function. AmiGO is a fairly simple and well organized website, which allowed for quick navigation between different GO terms. One aspect of gene ontology that is especially helpful is its listing of everything that has been associated with your gene of interest. Instead of laboriously sifting through the primary literature, a researcher can essentially observe everything their gene is involved with on one website, allowing for a more refined research approach. GO terms related to LDLR organized the protein's function and it will be useful for future research.